Misuse of Rear-Facing Infant and Convertible Car Seats
Fri 8 Nov, by FritzLaw on Personal Injury
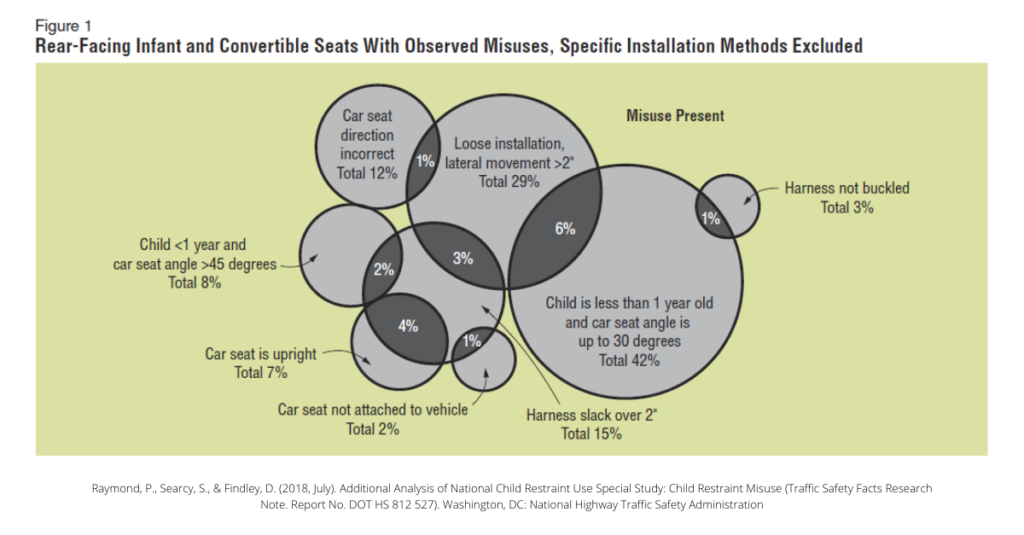
Car accidents happen around us on a daily basis. In 2018, there were 36,560 motor vehicle traffic fatalities in the United States.¹ It is no secret that properly wearing a seat belt while driving or riding in a car can help reduce the severity of injuries in the event of an accident. The same goes for children who are riding in the backseat of a car. When it comes to child safety, it is extremely important that the proper car seat is being used (per height and weight) and that the car seat is properly installed. A recent study in 2018 by the National Highway and Traffic Safety Administration showed that at least 49% of the cases observed had at least one misuse in regards to the installation or operation of a child’s car seat.² When it comes to rear-facing Infant and convertible car seats, the most common misuse was the seat angle (42%), specifically, when a child was less than one year old and the car seat was less that 30 degrees.² The next most common misuse was loose installation (29%), followed by harness slack being over 2″ (15%), the car seat being in the wrong direction (12%), the child being less than one year old with a seat angle of over 45 degrees (8%), an upright car seat (7%), the harness not being buckled (3%) and the car seat not being attached to the vehicle (2%).² The best way for you and your family to stay safe while riding in a car is to wear a seat belt and make sure that your children’s car seats are being used properly!
In the event that you or a family member is injured because of another driver’s actions on the road, please give us a call. We would love to help!
¹ National Center for Statistics and Analysis. (2019, October). 2018 Fatal Motor Vehicle Crashes: Overview. (Traffic Safety Facts Research Note. Report No. DOT HS 812 826). Washington, DC: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
² Raymond, P., Searcy, S., & Findley, D. (2018, July). Additional Analysis of National Child Restraint Use Special Study: Child Restraint Misuse (Traffic Safety Facts Research Note. Report No. DOT HS 812 527). Washington, DC: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
